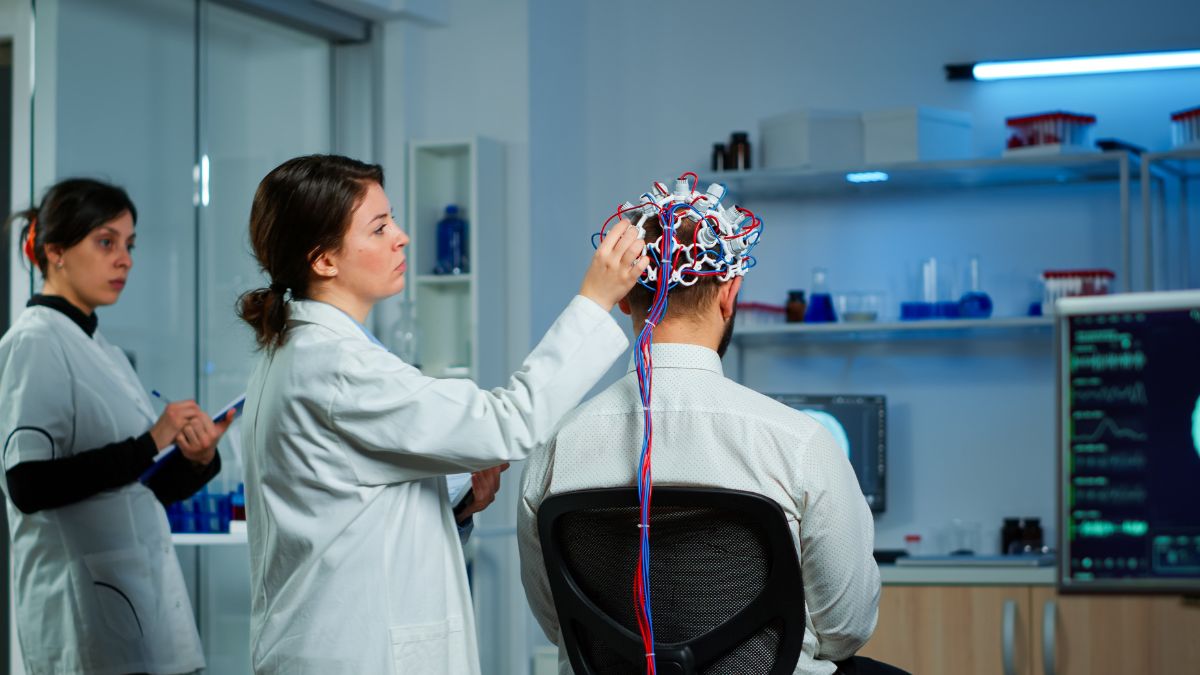
Neuromodulation is changing the way we approach some of the most challenging medical conditions. Imagine having the ability to regulate nerve activity to treat chronic pain, neurological disorders, or even mental health conditions. This advanced technology is reshaping healthcare, making it more precise and patient-focused. Let’s look into the fundamentals of neuromodulation, how it works, and its transformative impact.
Definition
Neuromodulation is the process of regulating nerve activity through targeted stimulation, either electrically or chemically. It focuses on altering the way nerves communicate to address specific medical conditions. This technology can work via implanted or external devices, delivering precision treatment with minimal side effects.
The underlying concept is straightforward: by fine-tuning the nervous system’s electrical signals, we can influence functions like pain perception, motor control, or even mood regulation.
Mechanism
At its core, neuromodulation relies on devices that send electrical or chemical signals to particular nerves or brain areas. These signals disrupt or enhance nerve activity, depending on the desired effect.
For instance:
- Electrical Stimulation: Tiny electrical pulses are delivered via implanted electrodes or external devices to alter neural activity.
- Chemical Stimulation: Medications or neurotransmitters are used to adjust nerve signals in targeted areas.
This precision is what sets neuromodulation apart from traditional treatments.
Applications
Pain Relief
Chronic pain is one of the leading reasons for neuromodulation use. Spinal cord stimulators, for example, help block pain signals before they reach the brain. This approach is highly effective for conditions like back pain or nerve damage that don’t respond well to medication.
Neurological Disorders
Conditions like Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis often involve disrupted neural communication. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) are two examples of neuromodulation therapies that reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Mental Health
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a non-invasive form of neuromodulation, is gaining traction in treating depression and anxiety. When traditional treatments like medication fail, TMS offers hope for patients.
Rehabilitation
Neuromodulation also supports physical rehabilitation by restoring motor function in stroke survivors or those with spinal cord injuries. It’s even being studied for applications like restoring bladder control.
Benefits
The greatest strength of neuromodulation is its precision. Unlike medication, which often has widespread effects, neuromodulation targets only the affected areas.
| Advantages | Details |
|---|---|
| Minimally Invasive | Most procedures involve minor surgeries or are entirely non-invasive. |
| Customizable | Devices can be adjusted to meet a patient’s specific needs. |
| Reversible | Implanted devices can often be removed or switched off if needed. |
| Reduced Side Effects | Compared to medication, there are fewer risks of systemic side effects. |
Challenges
While neuromodulation is exciting, it’s not without challenges. Devices can be expensive, limiting accessibility. There’s also a small risk of complications, such as infection or device malfunction. Moreover, ongoing research is needed to expand its applications further and refine existing technologies.
Future Potential
The future of neuromodulation is full of possibilities. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are making devices smarter and more responsive. Potential applications include treatments for memory loss, Alzheimer’s, and even enhancing cognitive performance.
Neuromodulation represents a shift toward precision medicine, offering hope to patients who’ve exhausted other options. Its ability to treat the root cause of conditions, rather than masking symptoms, is what makes it revolutionary.
FAQs
What is neuromodulation?
It regulates nerve activity using electrical or chemical signals.
How does neuromodulation work?
Devices send signals to nerves to adjust their activity.
What conditions can it treat?
It treats pain, epilepsy, mental health issues, and more.
Are devices reversible?
Yes, most neuromodulation devices are reversible.
What’s the future of neuromodulation?
It includes memory restoration and cognitive enhancements.