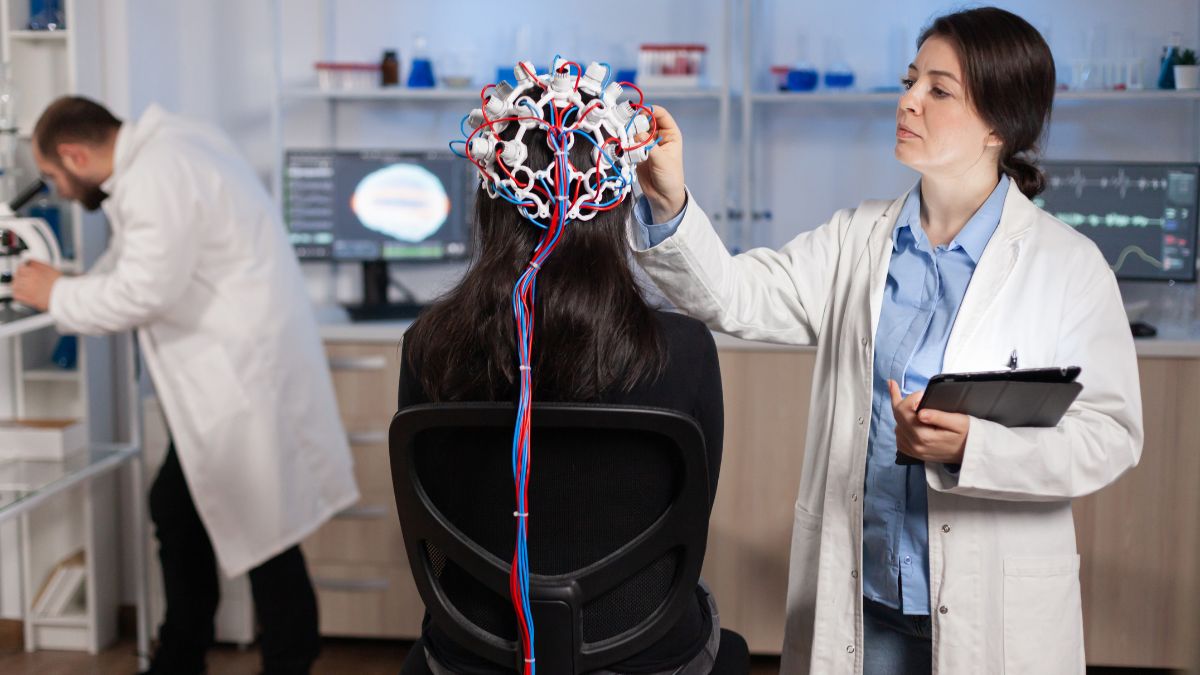
Neuromodulation is revolutionizing healthcare by offering innovative solutions to treat chronic conditions, neurological disorders, and even mental health issues. By targeting specific areas of the nervous system, this advanced technology addresses root causes rather than merely managing symptoms. Let’s break down how neuromodulation works, its applications, and the latest breakthroughs shaping its future.
What Is Neuromodulation?
Neuromodulation is the process of altering nerve activity through the application of electrical or chemical stimuli. The nervous system relies on electrical signals to communicate between the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body. Neuromodulation technology regulates these signals to restore balance and functionality.
Think of it as a finely tuned orchestra. When one instrument (or nerve signal) is out of tune, neuromodulation works like a conductor, ensuring every part performs in harmony again.
How It Works
Electrical stimulation is the most common form of neuromodulation. Devices such as spinal cord stimulators or deep brain stimulators (DBS) generate electrical pulses to modulate nerve activity.
- Pain Relief: Electrical signals block pain signals before they reach the brain.
- Neurological Disorders: Pulses regulate abnormal nerve activity, improving movement or reducing seizures.
Chemical Stimulation
In some cases, neuromodulation involves delivering chemical agents, such as neurotransmitters, directly to targeted nerves. This method adjusts nerve signaling chemically rather than electrically.
Key Applications
Chronic pain, especially conditions like back pain or nerve damage, is a major area where neuromodulation shines. Spinal cord stimulators (SCS) are often used to block pain signals at the spinal level, significantly reducing discomfort.
Neurological Conditions
Neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and dystonia benefit from devices like DBS and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS). These treatments can help manage tremors, seizures, and other symptoms that medications struggle to control.
Mental Health
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a non-invasive neuromodulation technique, has emerged as a game-changer for treating depression and anxiety, especially in patients unresponsive to traditional therapies.
Emerging Uses
Neuromodulation is expanding into areas like stroke rehabilitation, addiction treatment, and cognitive enhancement. Researchers are even exploring its potential to restore movement in spinal cord injury patients.
Recent Breakthroughs
The field of neuromodulation is advancing rapidly. Here are some of the most exciting developments:
- Closed-Loop Systems: These smart devices monitor neural activity in real time and adjust stimulation automatically, enhancing effectiveness and reducing side effects.
- Miniaturized Implants: Newer, smaller devices are easier to implant and more comfortable for patients.
- Expanded Applications: Researchers are investigating neuromodulation for Alzheimer’s disease, obesity management, and even improving memory.
Advantages
| Advantages | Details |
|---|---|
| Targeted Therapy | Stimulates only the affected nerves, minimizing side effects. |
| Non-Pharmaceutical | Reduces reliance on medications and their systemic risks. |
| Adjustable | Device settings can be tailored to individual needs. |
| Reversible | Many devices can be turned off or removed if necessary. |
Challenges
Despite its promise, neuromodulation isn’t without challenges. The cost of devices and treatments can be prohibitive, and there’s a risk of complications, such as infections or device failure. Additionally, not all patients respond to these treatments, and ongoing research is needed to optimize results.
The Future
The future of neuromodulation is incredibly exciting. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into devices to improve precision and personalization. Potential applications in memory restoration, cognitive enhancement, and even mood regulation could redefine what’s possible in healthcare.
Neuromodulation is more than just a medical advancement—it’s a glimpse into the future of medicine. By combining cutting-edge technology with a deep knowing of the nervous system, it offers hope to millions of patients worldwide.
FAQs
What is neuromodulation?
It alters nerve activity using electrical or chemical stimulation.
How does neuromodulation treat pain?
It blocks pain signals before they reach the brain.
Can neuromodulation treat depression?
Yes, TMS is effective for depression and anxiety.
What are closed-loop systems?
These devices adjust stimulation automatically based on neural activity.
What is the future of neuromodulation?
It includes cognitive enhancement and AI-driven precision treatments.