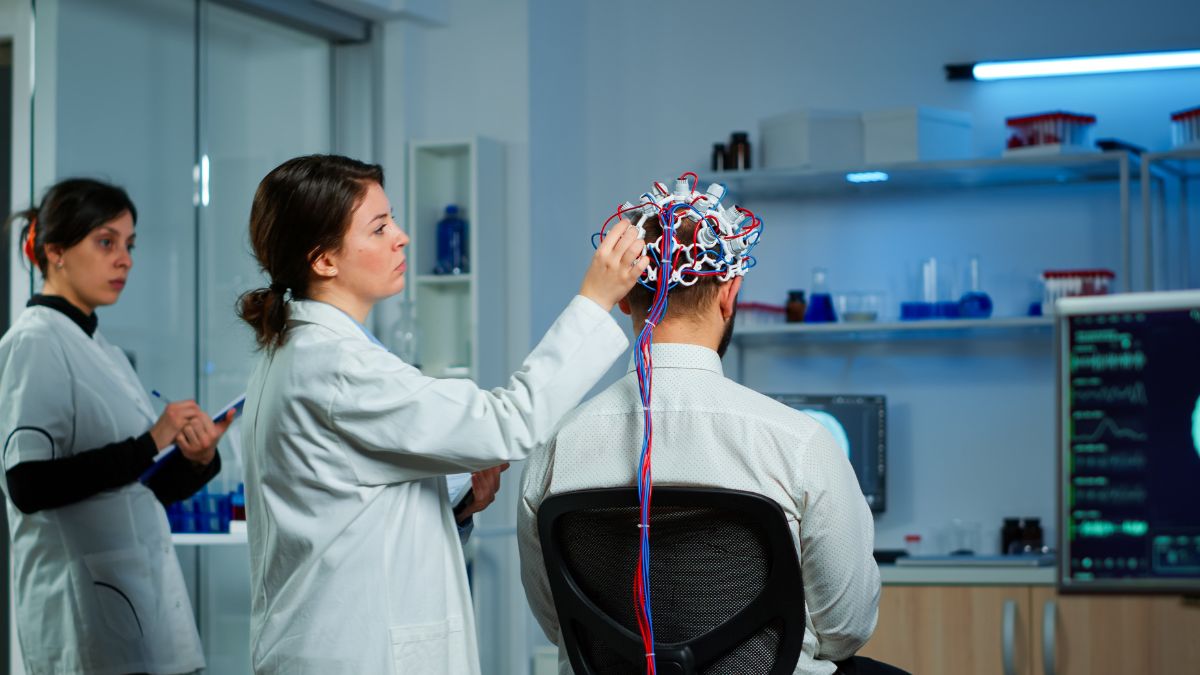
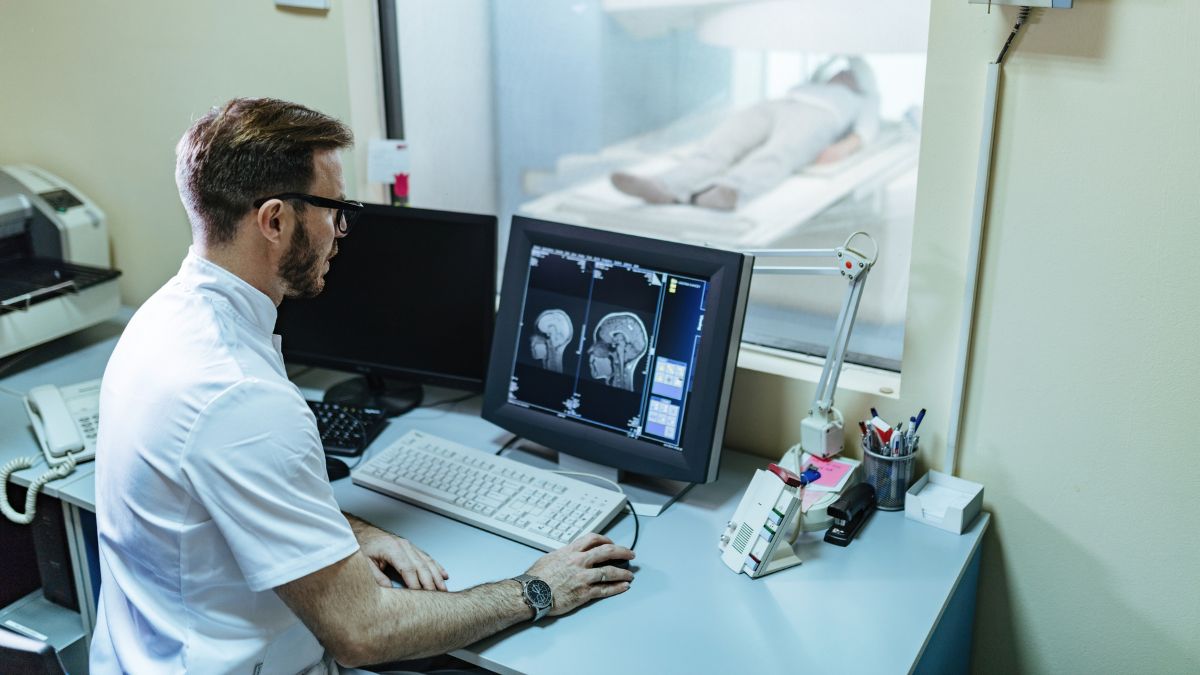
Neuromodulation is rapidly evolving, and wearable technology is playing a crucial role in making it more accessible, non-invasive, and user-friendly. Gone are the days when neuromodulation required complex surgical implants—emerging wearables are transforming the way we treat neurological disorders, chronic pain, and mental health conditions. From brain-stimulating headbands to nerve-stimulating wristbands, these cutting-edge innovations are redefining the future of healthcare. Let’s look into how wearable neuromodulation devices are changing lives and what possibilities lie ahead.
Neuromodulation
Neuromodulation involves the use of electrical or magnetic stimulation to influence nerve activity, helping to regulate brain and body functions. Traditionally, neuromodulation required surgically implanted devices, but with the rise of wearable technology, non-invasive alternatives are now available.
Wearable neuromodulation devices apply stimulation externally, making treatments safer, more comfortable, and easier to integrate into daily life. This shift is opening new doors for patients who were previously hesitant about invasive options.
Wearable Neuromodulation Devices
Several innovative wearable neuromodulation devices are making headlines, offering promising solutions for various medical conditions.
1. tVNS Devices
These devices stimulate the vagus nerve through the skin, helping regulate brain activity and reduce symptoms of neurological disorders.
- Used for: Depression, anxiety, epilepsy, migraines
- How it works: Small electrodes are placed on the ear or neck, delivering mild electrical pulses.
2. tDCS Headbands
These lightweight, portable headbands use mild electrical currents to enhance brain function and treat mental health conditions.
- Used for: Depression, cognitive enhancement, stroke recovery
- How it works: Low-level electrical currents stimulate specific brain regions to improve neural connectivity.
3. nSCS
Wearable spinal cord stimulators are providing pain relief without requiring surgical implants.
- Used for: Chronic pain, lower back pain, neuropathy
- How it works: A wireless device worn on the lower back sends electrical signals to modulate pain perception.
4. Electrotherapy Wristbands
These wearables use electrical pulses to stimulate nerves in the wrist, reducing symptoms of nausea and stress.
- Used for: Motion sickness, chemotherapy-induced nausea, anxiety
- How it works: Gentle electrical signals disrupt nerve pathways responsible for nausea and stress responses.
5. BCI Wearables
AI-powered BCIs are revolutionizing neuromodulation by allowing users to control devices using brain signals.
- Used for: Neurorehabilitation, paralysis, prosthetic control
- How it works: Electrodes detect brain activity and translate it into commands for assistive devices.
Traditional Methods
| Feature | Wearable Neuromodulation | Traditional Neuromodulation |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Requires surgery |
| Portability | Wearable, easy to use | Implanted, stationary |
| Customization | Adjustable settings | Pre-programmed |
| Risk Level | Low | Moderate (surgical risks) |
| Cost | More affordable | Expensive surgical implants |
Wearables provide an excellent alternative for those who want the benefits of neuromodulation without the risks associated with surgery.
Benefits of Wearable Neuromodulation
Wearable neuromodulation devices offer several advantages:
- Non-Invasive: No surgery or implants required.
- User-Friendly: Simple to use, making treatment more accessible.
- Portable: Can be used anywhere, improving convenience.
- Adjustable Therapy: Users can personalize stimulation levels.
- Reduced Side Effects: Fewer complications compared to implanted devices.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their promise, wearable neuromodulation devices still face some hurdles:
- Limited Power: Wearables provide milder stimulation than implanted devices, which may reduce effectiveness for severe cases.
- Battery Life: Frequent charging may be required for continuous use.
- Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution: Some patients may still need implantable options for optimal results.
However, ongoing research is addressing these challenges, with new advancements improving efficiency and effectiveness.
Future of Wearable Neuromodulation
The future of wearable neuromodulation looks incredibly promising. Innovations in AI, machine learning, and miniaturized electronics are expected to enhance functionality, making devices smarter and more personalized.
Some exciting future possibilities include:
- AI-Powered Wearables: Devices that learn user patterns and automatically adjust stimulation in real-time.
- Wireless, Battery-Free Devices: Energy-harvesting wearables that eliminate the need for charging.
- Multi-Condition Therapy: Single devices capable of treating multiple neurological and physical conditions.
With continued advancements, wearable neuromodulation will become an essential tool for treating a wide range of conditions, making therapy more accessible and effective than ever before.
If you’re looking for a non-invasive way to manage neurological conditions, wearable neuromodulation may be the breakthrough solution you need. The future of healthcare is here, and it’s wearable.
FAQs
What is wearable neuromodulation?
It’s a non-invasive way to stimulate nerves using external devices.
Which conditions can wearable neuromodulation treat?
It helps with chronic pain, depression, anxiety, epilepsy, and more.
How do wearable neuromodulation devices work?
They use electrical or magnetic stimulation to regulate nerve activity.
Are wearable neuromodulation devices safe?
Yes, they are generally safe with minimal side effects.
What is the future of wearable neuromodulation?
Future advancements include AI-powered, wireless, and multi-condition devices.