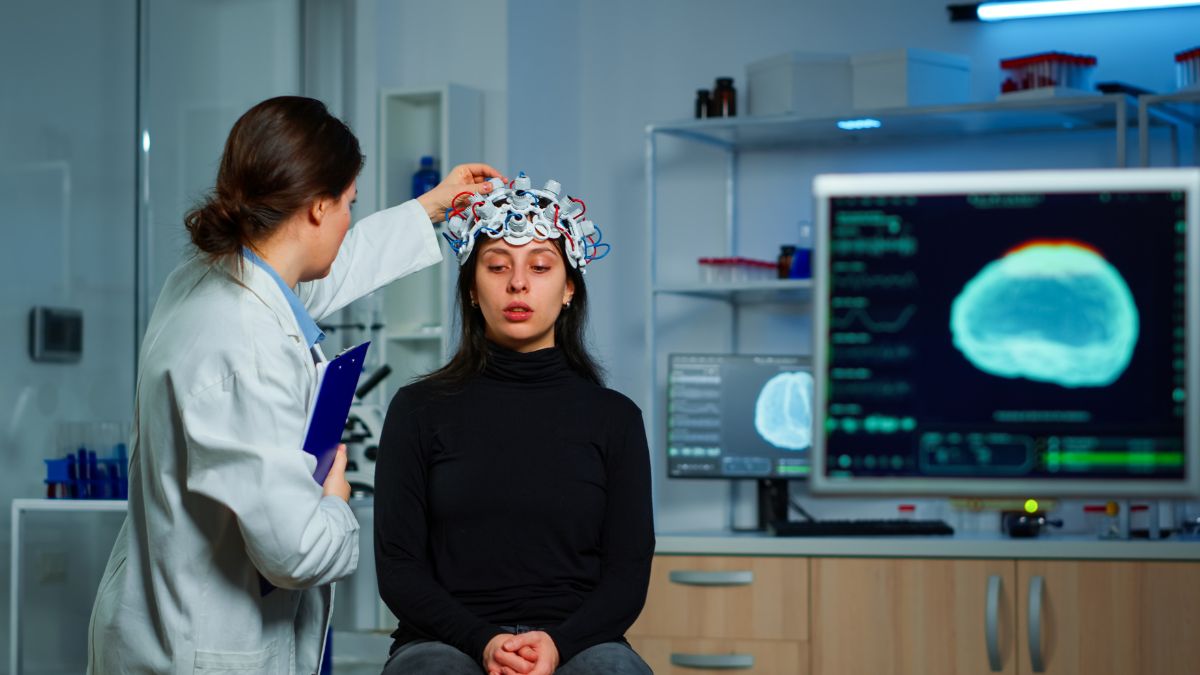
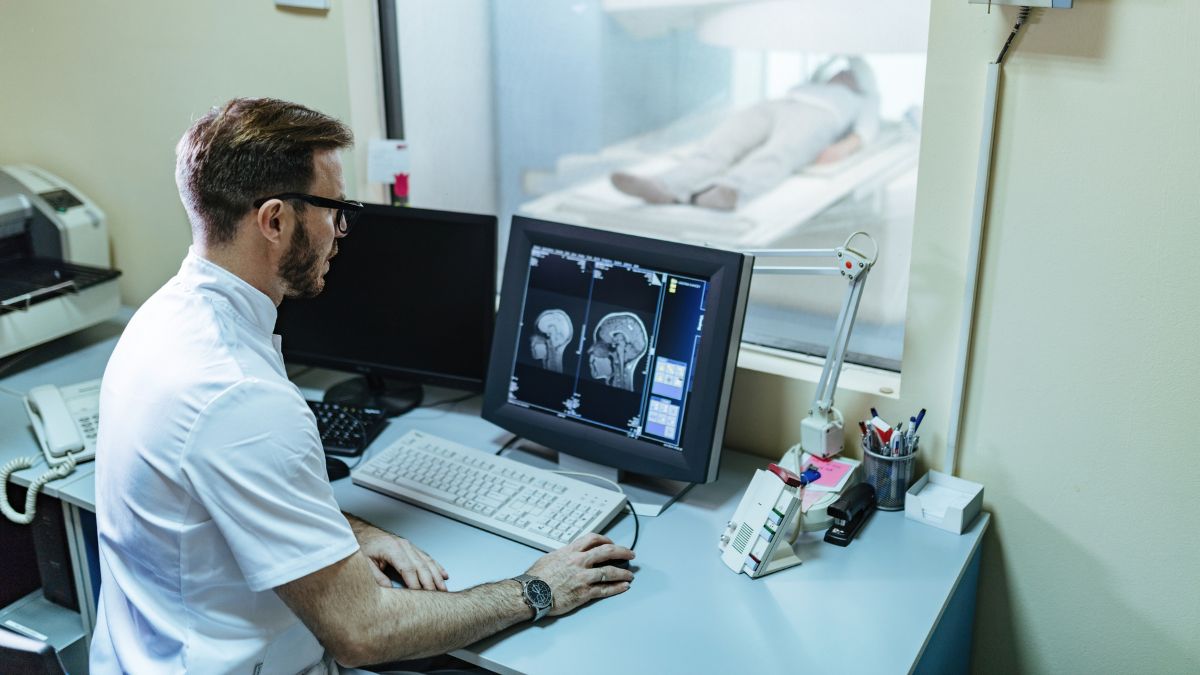
Neurological disorders can feel like an uphill battle for those affected, impacting not just physical health but mental well-being too. With traditional treatments often offering limited relief, many patients are left searching for a better way forward. Enter neuromodulation—a cutting-edge technique that’s reshaping the landscape of neurological care. This innovative approach offers hope for managing complex conditions in ways once thought impossible.
Neuromodulation
Neuromodulation refers to the use of electrical or magnetic stimulation to influence nerve activity in the body. Essentially, it’s a high-tech way to regulate how the nervous system functions. The technique involves implanting small devices or using external systems to deliver precise signals to specific areas of the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nerves.
Think of neuromodulation as fine-tuning a musical instrument—by targeting problem areas, it helps the nervous system “play” better. While it doesn’t cure neurological disorders, it can drastically improve symptoms and enhance quality of life.
Benefits
Why is neuromodulation such a big deal? For starters, it’s versatile. It’s already being used to treat a wide range of neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, chronic pain, and even depression. Another huge advantage? It’s a minimally invasive alternative to surgeries, offering fewer risks and shorter recovery times.
Here’s a breakdown of some key benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Symptom Relief | Reduces tremors, seizures, and pain. |
| Minimally Invasive | Low-risk alternative to major surgeries. |
| Medication Reduction | Decreases reliance on drugs. |
| Adjustable | Settings can be fine-tuned to suit needs. |
Applications
Neuromodulation is currently making waves in treating various conditions:
- Parkinson’s Disease: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) helps control tremors and stiffness.
- Epilepsy: Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) reduces seizure frequency.
- Chronic Pain: Spinal cord stimulators interrupt pain signals for long-term relief.
- Mental Health: Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is effective for depression and OCD.
What makes these applications remarkable is their adaptability. Doctors can adjust the stimulation to meet each patient’s unique requirements, ensuring a personalized approach.
Challenges
Of course, no treatment is perfect. Neuromodulation does come with challenges, including high costs and potential risks like infection or device malfunction. Additionally, not every patient responds to the therapy, and identifying the right candidates requires careful evaluation.
Insurance coverage can also be a sticking point, with out-of-pocket expenses posing a barrier for some patients. That said, the technology is advancing rapidly, and accessibility is expected to improve over time.
Future
The future of neuromodulation looks incredibly bright. Research is underway to develop even more precise systems, such as closed-loop devices that automatically adjust stimulation in real time. Imagine a device that could sense your symptoms and respond instantly—pretty amazing, right?
Additionally, scientists are looking into the use of neuromodulation in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and stroke recovery, expanding its potential impact. As these advancements unfold, neuromodulation is set to become an indispensable tool in the fight against neurological disorders.
Living with a neurological disorder doesn’t have to mean settling for limited options. Neuromodulation offers a groundbreaking approach that’s changing lives every day. If you or someone you know is struggling with a neurological condition, this innovative therapy could be the key to a brighter future.
FAQs
What is neuromodulation?
Neuromodulation uses electrical or magnetic signals to regulate nerve activity.
Which conditions can neuromodulation treat?
It helps manage Parkinson’s, epilepsy, chronic pain, and depression.
Is neuromodulation permanent?
Devices can be adjusted or removed if needed, offering flexibility.
What are the risks of neuromodulation?
Risks include infection, device malfunction, or therapy ineffectiveness.
Is neuromodulation covered by insurance?
Many plans cover it, but some out-of-pocket costs may apply.